FERTILIZATION PROCESS IN MAMMALS
Definition
Fertilization is the process of union of mature male gamete (sperm) with mature female gamete (ovum) to produce new cell of life which is called (zygote) through chain of events in the oviduct (fallopian tubes). Indeed, interruption of any event will cause fertilization failure.
By the end of the follicular phase the mature follicle will develop and rupture, excrete the oocyte with some granulosa cells into oviduct. The oocyte is now competent to undergo fertilization.
Ruptured follicle will transformed into the corpus luteum, that produce large amount of progesterone that helps to prepare the uterus for implantation of fertilized egg
Mechanisms of ovum transport:
a) Fimbria on terminal oviduct--acts as funnel to receive ovum
b) Fluids (abdominal cavity and that escaping from follicle during ovulation) serve as medium for free-floating ovum
c) Cilia lining oviduct and muscular contractions assists in moving ovum to site of fertilization
d) The site of fertilization on most farm animals is (ampullary-isthmic junction) while in human is (ampulla) region.
a) Sperm capacitation:
Freshly ejaculated sperm are unable to fertilize an egg. Rather, they must first undergo a series of changes known as capacitation. Capacitation is associated with removal of adherent seminal plasma proteins, reorganization of plasma membrane lipids and proteins.
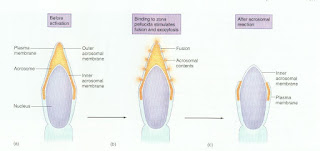
b) Acrosome reaction:
The acrosome reaction involves breakdown and fusion of outer acrosome membrane with the plasma membrane of the sperm. This results in formation of vesicles and release of enzymes needed for sperm to penetrate the cumulus oophorus and corona radiata as well as zona pellucida . during the penetration process the acrosome is lost with only the inner acrosomal membrane remaining around the sperm head.
c) Sperm penetration:
Sperm cell penetrate cumulus oophorus by the enzyme (hyaluronidase) released during acrosome reaction
Sperm cell penetrate corona radiata by the enzyme (corona-penetrating enzyme) also released during acrosome reaction.
Sperm cell penetrate zona pellucida by the acrosin (trypsinlike enzyme) also released during acrosome reaction.
Then membrane of sperm fuses with the vitelline membrane of the egg, the egg cytoplasm around the area of contact surrounds the sperm head and incorporating it into the egg
The nucleus of sperm is then release into the egg cytoplasm without the tail
d) Consequences of fertilization:
In most mammals after releasing the sperm nucleus into egg cytoplasm it stimulates the diffusion of cortical granules into the previtelline space, the erection of a barrier to prevent fertilization by more than one sperm will occur, this process is called zona reaction and vitelline block.
Then the male and female pronuclei are formed and unite (syngamy) to establish the diploid one cell zygote.

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt,please let me know.